
It’s getting harder to deal in some of the world’s most important commodities as everything from geopolitical turmoil to exchange snafus prompt traders to rush for the exits, rapidly draining liquidity.
Prices of materials like crude, gas, wheat and metals have become alarmingly erratic as a gulf emerges between buyers and sellers who are facing big financing strains. Markets have been roiled on fears about Russia’s invasion of Ukraine constraining commodities flows, though in many cases rallies were quickly followed by a drop in prices.
The volatility is particularly difficult to navigate because some moves appear to defy fundamentals, with hedge funds exiting long-term bullish bets just as supply looks the tightest in years. Merchants are finding it harder to snap up any cheap cargoes because of huge margin calls and credit line caps.
“Volatility as an asset class is enormous now, and on top of that you have some serious operational issues,” said Ilia Bouchouev, a Pentathlon Investments partner and adjunct professor at New York University. “It’s a vicious loop where volatility forces companies to reduce positions, which means what’s left in the market is forced trading. That in turn contributes to even more volatility.”
Metals mayhem
Ructions from the Ukraine war have been compounded by a historic nickel short squeeze. The LME suspended trading as prices surged 250% to a record, canceling almost $4 billion of transactions.
That caused uproar among investors who stood to profit from bullish bets prior to last week’s closure — and snags with the reopening have hardly improved the mood. Many previously bullish investors are now in a long queue of sellers enduring sharp price drops while they wait for buyers.
By late Thursday, almost $3.3 billion of nickel was on offer at the limit-down price, but there wasn’t a single bid on the LME’s order book. Just two trades took place that day in the electronic market. The illiquidity is a worry for consumers who use nickel in stainless steel and electric-vehicle batteries.
There are signs of contagion as trading in other metals also slumps. That’s bad news for manufacturers and end users as it could leave them exposed to more violent price swings.
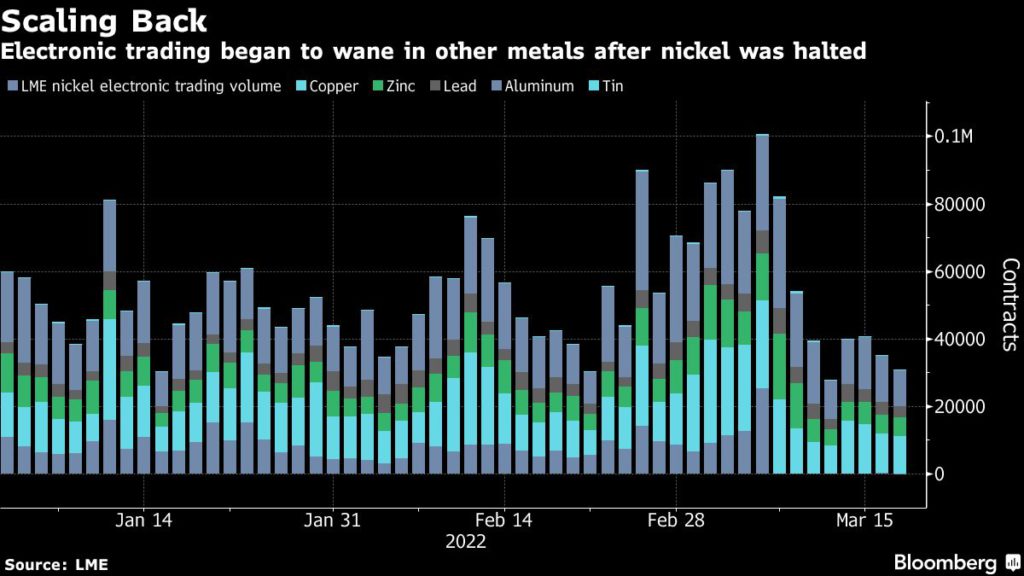
There are signs of spillover in specialist instruments LME traders use to manage price risks. Three long-standing participants in the options market said it’s become much harder to secure quotes from dealers in recent days and that trading spreads between contracts is increasingly erratic.
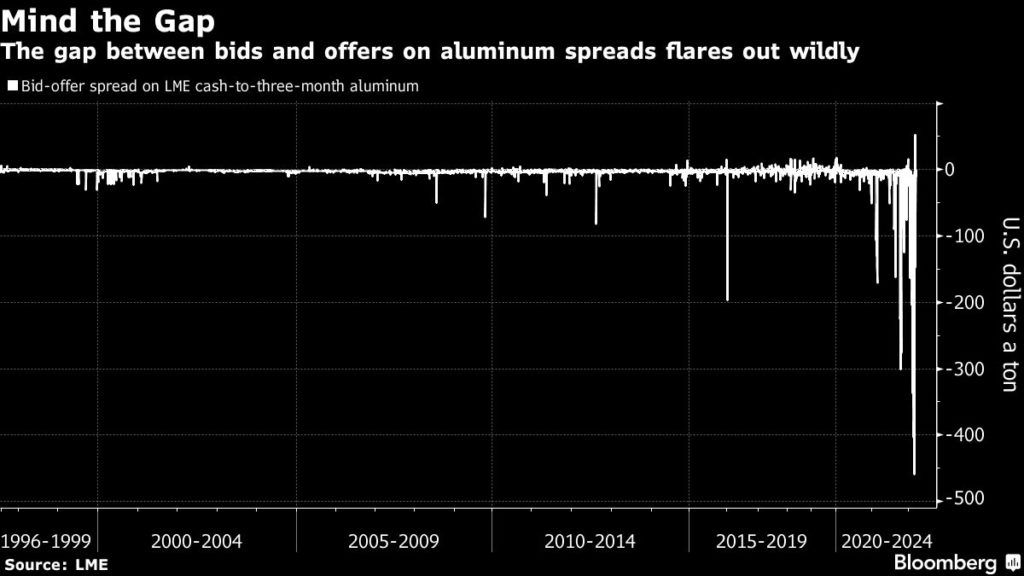
In aluminum, dealers say scarce liquidity is sparking wild moves in prices between key contracts, such as the cash-to-three-month spread. For that spread, which was at about $17 on Thursday, bids and offers are now frequently hundreds of dollars apart.
Traders say the gap is due to electronic bids that were likely placed by algorithmic traders, because in practice the spread shouldn’t reach such extreme levels. But with low liquidity and many specialist traders and hedge funds stepping back, those low-ball orders are often the only ones to appear on the screen.
Crude chaos
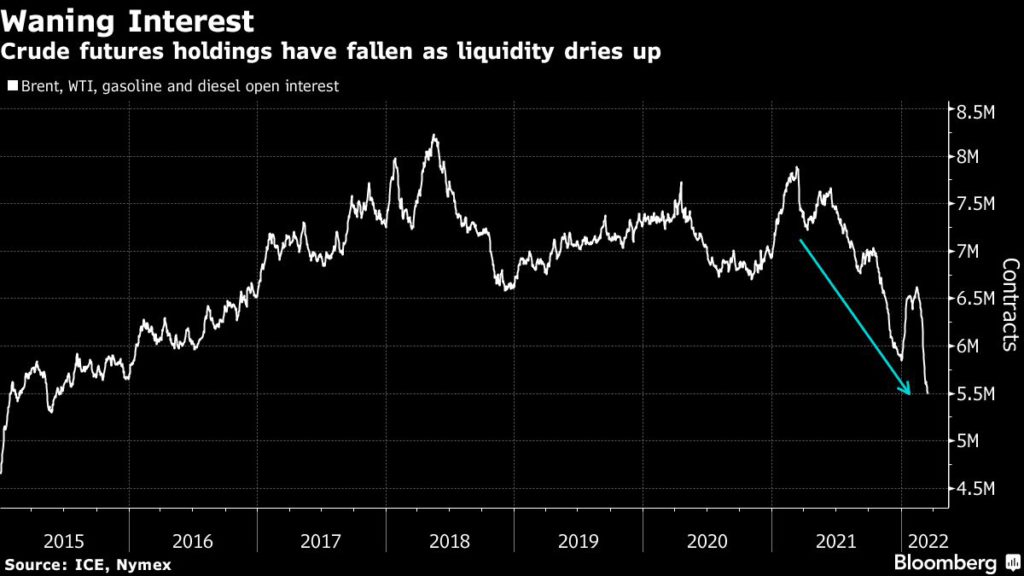
There are clear signs traders are pulling back. Combined open interest on main crude and refined product contracts have hit the lowest since 2015. Almost 1 billion barrels of contracts were liquidated in a period that saw Brent post 16 consecutive $5-a-barrel intraday swings — its longest such run ever.
“When prices can move $10 per barrel in either direction three times a day, no one can warehouse overnight risk and market makers are disappearing,” Energy Aspects analysts including Amrita Sen said.
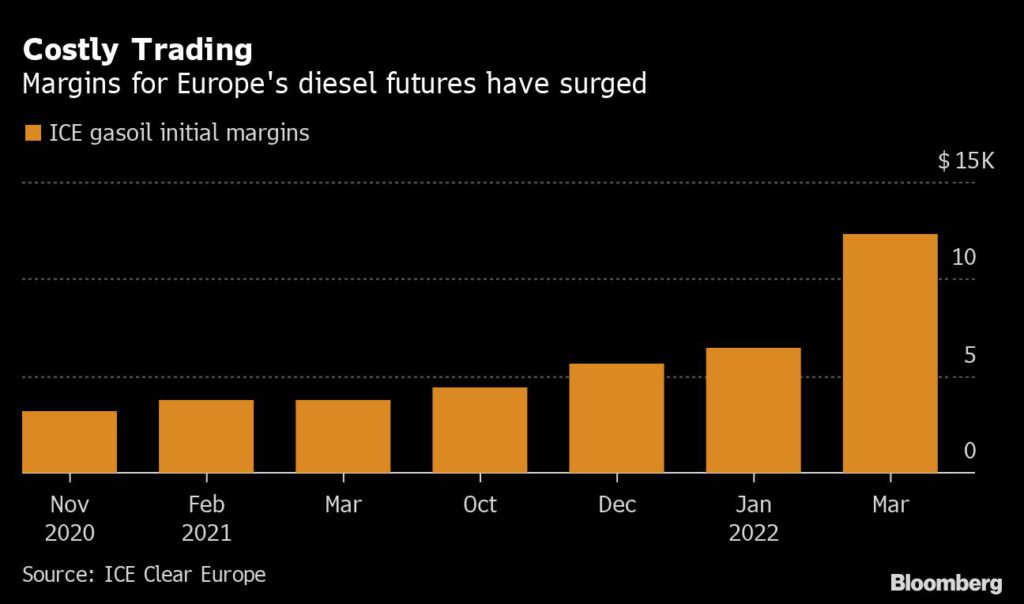
Clearinghouses have boosted initial margins — the collateral traders put up to finance their positions. In the case of gasoil, that meant traders had to stump up almost twice as much cash to trade the same amount.
Traders said they’re scaling back positions and not holding them for as long due to the volatility.
Gas tumult
On one day this month, benchmark European gas traded in a range of 140 euros ($155) a megawatt-hour — more than the contract costs now. With the swings spooking traders, open interest is near a two-year low.
Even before the Ukraine war, Europe’s gas and power markets were extremely turbulent due to concern about a winter supply crunch. Surging costs forced German energy giant Uniper SE to borrow $11 billion to pay down margins calls. German utility Steag GbmH and Norway’s Statkraft AS also had to boost liquidity.
Skyrocketing gas prices “require significant cash,” said Alfred Stern, who runs Austrian oil and gas company OMV AG. “So far, we were able to manage that in quite a good way, but it has been significant in the last couple of weeks here, lets say in the three-digit kind of millions that we had to inject.”
Crop trading
Chicago wheat volumes soared at the start of the war in Ukraine as prices climbed toward a record, but have this week slumped. In Kansas City wheat — the type closest to what Russia grows — open interest hit the lowest since 2015.
(By Mark Burton and Alex Longley, with assistance from Michael Hirtzer, Isis Almeida and Vanessa Dezem)
No comments:
Post a Comment